Sprocket and Hub Bolt Analysis on Slip-Critical Mining Equipment
Analysis
Objective
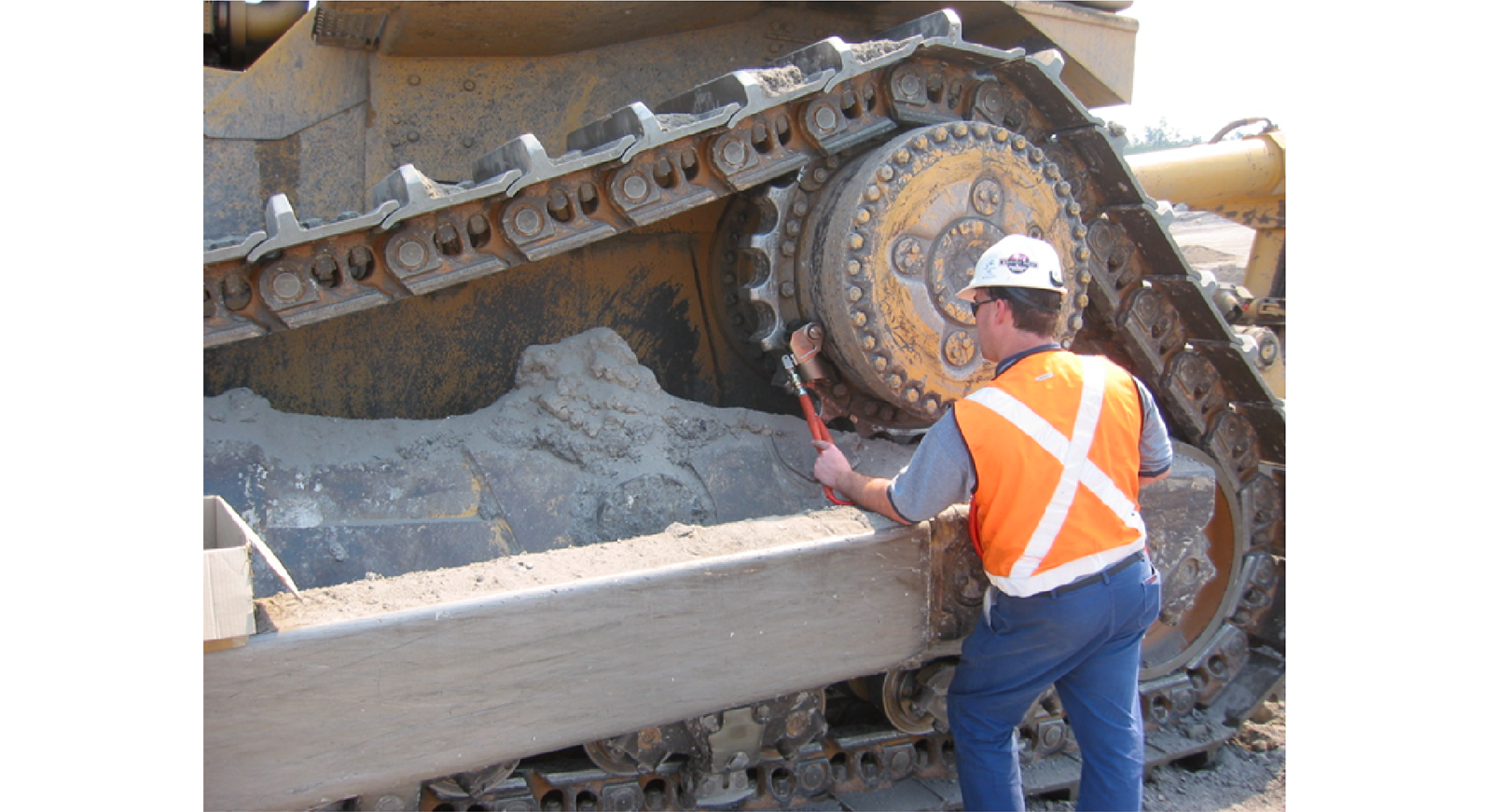
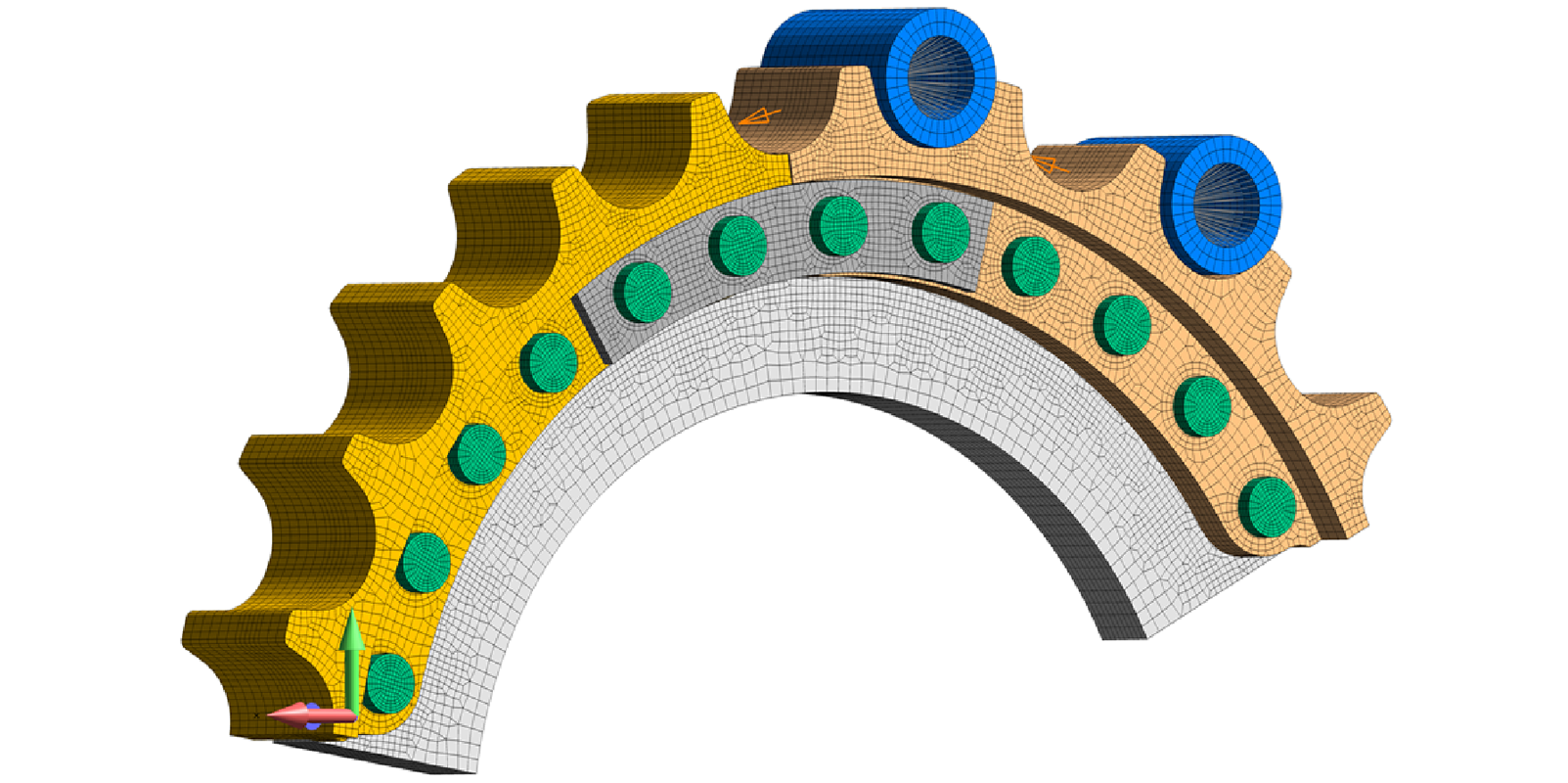
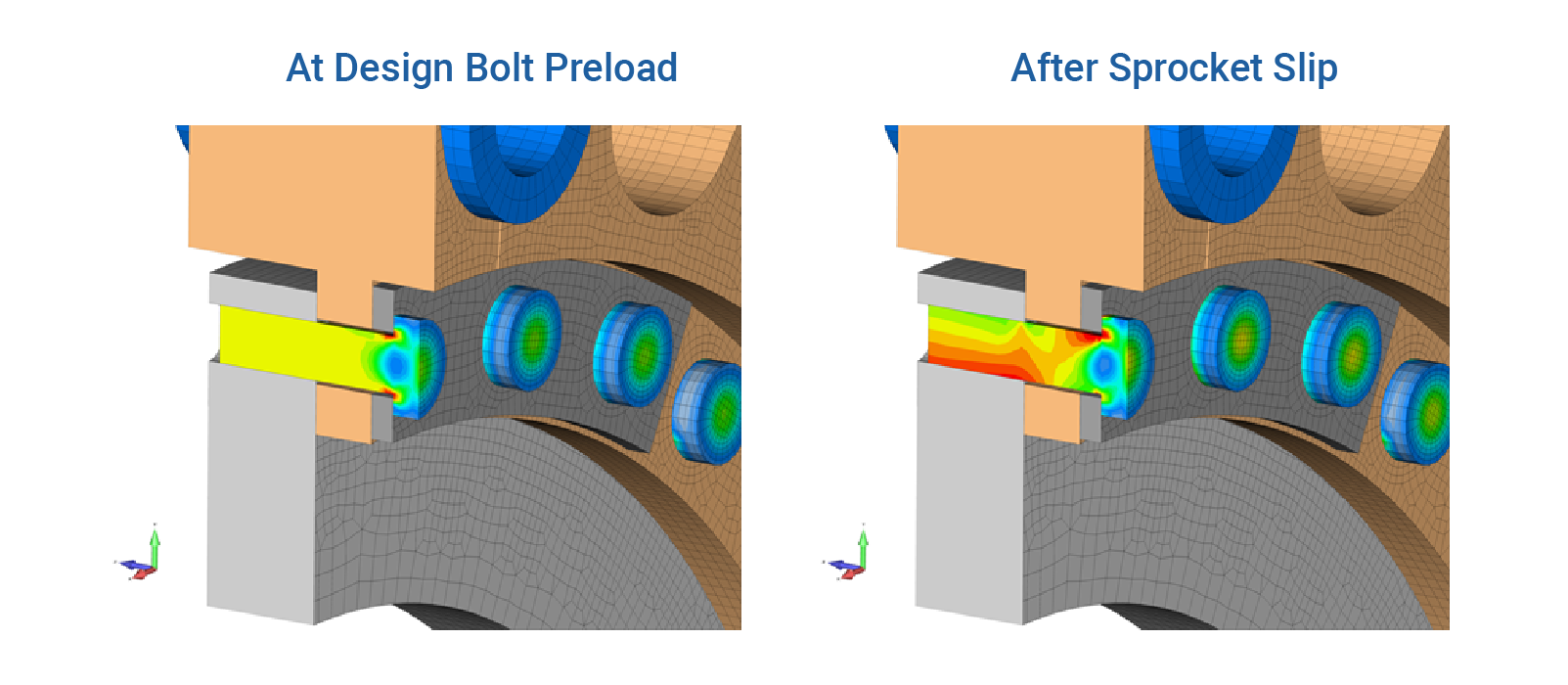
A typical design for large sprockets found on earth moving equipment and large conveyors, is to bolt the segmented sprocket onto a hub. Over time, as the sprockets are worn out, they can be replaced on-site without extensive downtown. These segments are bolted onto the hub and the chain load is ideally transferred by friction between the face of the sprocket onto the hub; thereby leaving the bolt in a perfect state of friction. If the design load is exceeded (i.e., excessive chain load), the sprocket can slip and the bolt is then placed in bending.
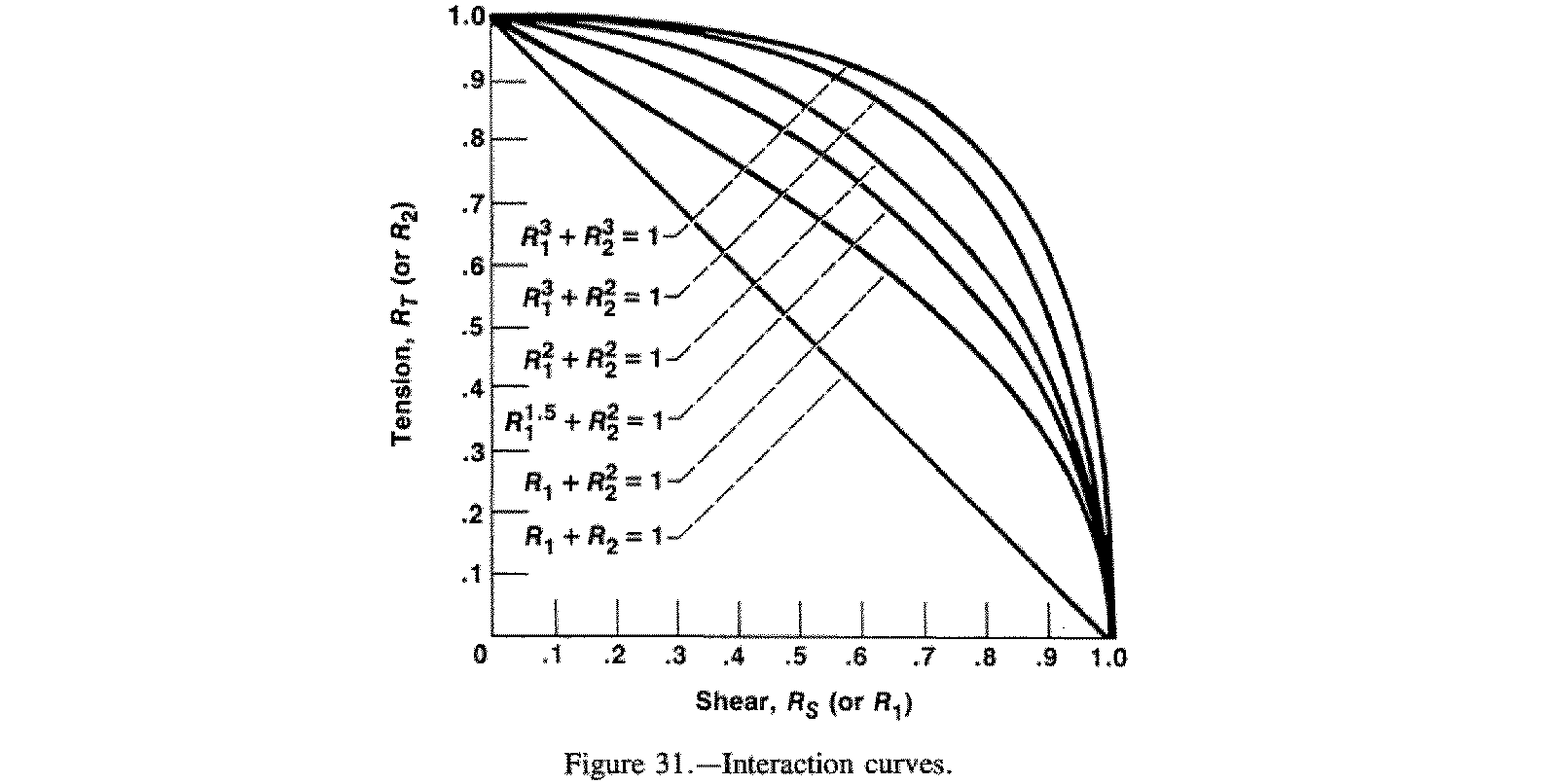
This project analyzed a large segmented sprocket and hub system under various chain loading conditions and interpreted the bolt stresses using the NASA 1228 bolt design criterion along with the MIL-HDBK-5J standard. Bolt sizing and preload recommendations could then be made to ensure slip critical design requirements were met.
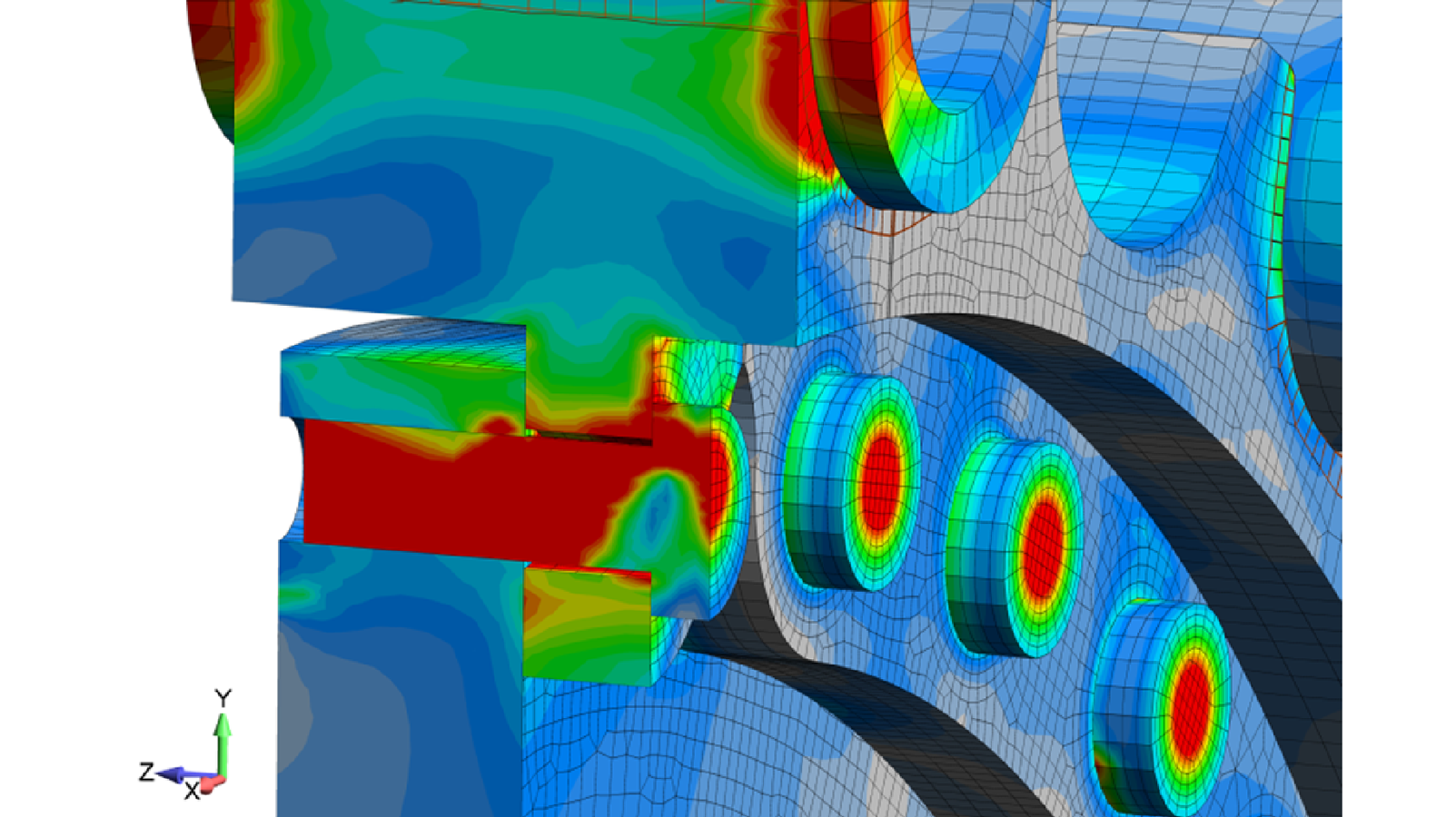
The FEA model captured the complete chain load to sprocket to hub load line behavior through the use of contacting surfaces between all mating parts. The model used a mix of high density brick elements along with a carefully graded mesh of 10-node tetrahedrals. Through careful construction, the model was able to generate complete chain load to final converged state analyzes in a matter of minutes. This was an important consideration since a design matrix approach (Design of Experiments) was required to determine the sensitivity of the design to friction, bolt preload and reinforcement design modifications. The sensitivity analysis indicated that the most effective approach to ensure a slip critical design with large sprockets is to ensure the highest possible bolt preload.
Keywords: Bolted joints, bolted connections, slip critical bolt design, bolt preload, FEA of bolted joints, stress and fatigue analysis of bolts, NASA 1228 bolt analysis, Analysis of bolted sprocket and hub designs, nonlinear contact with friction, FEA stress and fatigue analysis of bolts, Bolt margin of safety calculations for preloaded bolted connections,
PDF Download